If we say, the Model T embodies Henry Ford's lifelong goal - to make cars accessible to ordinary people. So now, millimeter wave radar manufacturers will also achieve their goals in the field of smart driving - making smart driving accessible to everyone.
Summary
Since the boom in smart driving entrepreneurship that started in 2016, RobotTaxi has been at its peak. Now it is facing a cold winter in the industry. Layoffs, bankruptcies, and market value plummets are common. The representative event is that Waymo, a subsidiary of Google, is launching a layoff plan. Tucson, the “first self-driving stock” Future (TSP, NASDAQ) shares have fallen by 98% since its listing.
Indeed, the current development of the autonomous driving market represented by RoboTaxi is not satisfactory. Perhaps the answer lies mainly in price: the price of a high-end autonomous driving system is so high that it exceeds the actual driving assistance or autonomous driving performance it can provide, and will only become the "appendix" in Musk's eyes.
The industry and capital circles have discovered that no matter how sexy and beautiful the story of intelligent driving is, performance and cost should be the common goals at the moment, especially in the context of this year's wave of OEM price cuts.
Performance improvement: 4D imaging millimeter wave radar stands out
Limited by the high cost of lidar, 4D imaging millimeter-wave radar (hereinafter referred to as "4D imaging radar") has become a hot topic in the field of intelligent driving this year.
Especially when Musk officially announced the addition of 4D imaging radar to the HW 4.0 platform hardware, it stirred up waves with one stone. Many mid- to high-end automobile manufacturers have begun to incorporate higher-accuracy 4D imaging millimeter-wave radar into their sensing solutions, including major manufacturers like BYD.
Before discussing the performance advantages of millimeter wave radar, let's first understand its working principle. Millimeter wave radar sends electromagnetic waves to the target and then receives the reflected electromagnetic waves. Based on the time difference of the reflected electromagnetic waves, it calculates the distance of the object. By comparing the frequency difference between sent and received electromagnetic waves, the speed of an object can also be calculated. This is a basic 2D millimeter wave radar that can measure the [distance] and [speed] of an object.
3D millimeter wave radar adds azimuth angle measurement on the basis of 2D, and can know the direction of the object on the [horizontal plane]. The 4D imaging radar adds [height] measurement on the basis of 3D, so it can obtain the complete three-dimensional information of the object, as well as the object's speed. These four dimensions of data together constitute 4D.
It can be seen that 4D imaging radar has the following advantages in terms of performance:
The first is high accuracy: after adding height measurement, 4D imaging radar can detect objects more accurately, reducing misjudgments and omissions, thereby improving the safety of autonomous driving.
The second is high resolution: In terms of resolution, 4D imaging radar can already approach 16-32 line lidar, which can depict objects in the environment in more detail and is more suitable for combination with deep learning frameworks.
In terms of strong anti-interference ability and large detection range, 4D imaging radar capabilities are also quite outstanding. This is mainly because millimeter wave radar is not affected by weather and light, which allows it to work normally in bad weather and at night, ensuring the stability of the autonomous driving system; it is not affected by the color and material of objects, and has a longer range. , the penetration is also stronger.
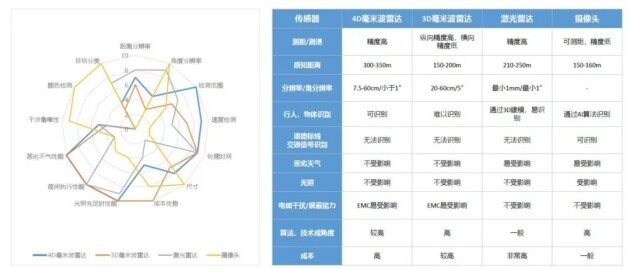
Image source: IDTechEX Research, online public channels
The underlying principles of 4D imaging radar are similar to the underlying technology of ordinary millimeter wave radar. A typical radar system uses a set of antenna elements, each with a wide beam. They can then digitally combine these through a process called digital beamforming to create an array of narrow beams, improving the resolution of the final image.
The difference between 3D and 4D radar is the arrangement of these antenna elements. A 3D radar system has horizontally arranged antennas, while a 4D radar has horizontally and vertically arranged elements.
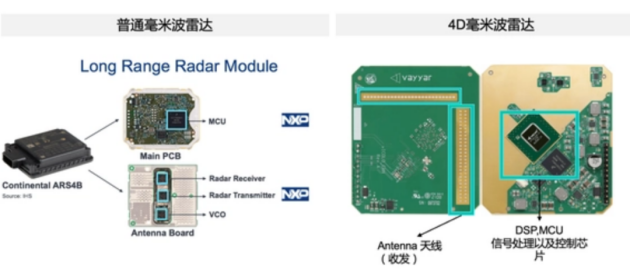
There are three mainstream technologies for 4D millimeter wave radar to implement point cloud functions:
The first is MIMO chip cascade. Traditional millimeter wave radar chip suppliers mostly use a multi-cascade approach based on 79GHz standard radar chips to improve power and angular resolution.
The second type: by integrating multiple transmitting and receiving antennas into one chip and developing a chipset to achieve the above functions. This solution is actually similar to chip cascade, but by further integrating antennas, MMICs, etc. to the chip level, the radar can be further miniaturized.
The third type: software algorithm empowerment. Software algorithms can directly act on MIMO links to virtualize more signal channels. The implementation methods can be simply summarized as: frequency modulation, phase modulation, and amplitude modulation.
In summary, 4D imaging millimeter-wave radar increases the number and density of antennas, optimizes angle and speed resolution, and outputs point cloud images that are denser, can depict more realistic environmental images, and can effectively analyze measured targets. It can adapt to more complex roads, identify more small objects, and effectively realize the monitoring of occluded objects and stationary or horizontal objects.
Cost reduction: Helping popularization of high-end intelligent driving
As the penetration rate of intelligent driving of new energy vehicles continues to increase, it is difficult to widen the technical gap in assisted driving. Urban NOA (Navigate on Autopilot, high-end intelligent driving assistance) has become the focus of competition among OEM manufacturers, such as Xiaopeng and Wei Lai, Nezha and Zhiji have launched their own NOA products. Therefore, 2023 is called the first year of urban NOA in the industry.
On November 2, 2022, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology and the Ministry of Public Security issued the "Notice on Carrying out the Pilot Work on the Access and Passage of Intelligent Connected Vehicles (Draft for Comments)". This is the first time that the central government has launched management measures and policies for L3/L4 level autonomous driving. It is also promoting the implementation of high-end intelligent driving.
According to the "McKinsey China Automotive Consumer Insights" report, consumers currently have high demand for autonomous driving functions in specific scenarios such as highways. Users, products, and policies are all driving the implementation of high-end intelligent driving.
4D imaging radar not only retains the performance characteristics of traditional millimeter wave radar - it has speed sensing capabilities, all-weather characteristics and low cost, but can also rely on sufficient information to integrate with visible light cameras, lidar and other sensors to help High-end intelligent driving is popularized.
Compared with lidar, the angular resolution of 4D imaging radar has reached 1-2 degrees, basically reaching the level of 8-16 line lidar, and some even reaching the 32-line level. The current price of 4D imaging radar is about US$200, and that of lidar is as high as US$500-1,000. As technology iterations reduce costs and scale effects reduce costs, the price of 4D imaging millimeter-wave radar is expected to drop to several hundred yuan, which has a huge cost advantage and will replace medium and low-line beam lidar.
Compared with 3D millimeter wave radar, although the price of 4D imaging radar is about 2-3 times higher than that of 3D millimeter wave radar, 4D imaging radar has the advantages of multi-dimensional data, high resolution, and high performance of point cloud images. Its massive signal level The release of information improves the integrity of the output information, facilitates pre-fusion of multi-sensors, and is more suitable for combination with artificial intelligence deep learning frameworks.
Therefore, driven by technology iterations and policies of manufacturers, the popularity of high-end intelligent driving will accelerate, and 4D imaging radars with both performance and cost advantages will be mass-produced and put into cars faster. According to Yole’s prediction, the future cost target of 4D radar will be US$100. This means that even low-end models will soon be able to use L2+ level intelligent driving solutions.

Image source: Data Bridge Market Research
In 1908, Henry Ford launched the world-famous Model T, ushering in the automobile age and a new era for Ford. In fact, the birth of the Model T was not only an innovation in vehicle type or design, but also an epoch-making innovation in the production methods of automobiles and even large-scale industrial production methods.
If we say, the Model T embodies Henry Ford's lifelong goal - to make cars accessible to ordinary people. So now, millimeter wave radar manufacturers will also achieve their goals in the field of smart driving - making smart driving accessible to everyone.
Opportunities: The rise of local supply chains, import substitution and long-term opportunities in overseas markets
According to Yelo's forecast, the global 4D millimeter wave radar market will reach US$3.5 billion in 2027. Seeing that the tens-billion-level market is just around the corner, capital has repeatedly extended an olive branch to millimeter-wave radar manufacturers. Since this year, several millimeter-wave radar rookies have received financing:
For example, NIO Capital and Beijing Xiaomi Intelligent Manufacturing Fund invested in 4D imaging radar start-up Sion Lingli in April this year; also in April, Makino Microelectronics, an early developer of 4D high-precision imaging radar, also announced the completion of a 100-million-yuan Pre -Series A financing.
Previous article:Sensata Technologies-EMB Braking Force Sensor
Next article:Xinwangwei-KungFu core automotive-grade MCU KF32A136
- Popular Resources
- Popular amplifiers
- Car key in the left hand, liveness detection radar in the right hand, UWB is imperative for cars!
- After a decade of rapid development, domestic CIS has entered the market
- Aegis Dagger Battery + Thor EM-i Super Hybrid, Geely New Energy has thrown out two "king bombs"
- A brief discussion on functional safety - fault, error, and failure
- In the smart car 2.0 cycle, these core industry chains are facing major opportunities!
- The United States and Japan are developing new batteries. CATL faces challenges? How should China's new energy battery industry respond?
- Murata launches high-precision 6-axis inertial sensor for automobiles
- Ford patents pre-charge alarm to help save costs and respond to emergencies
- New real-time microcontroller system from Texas Instruments enables smarter processing in automotive and industrial applications
- Innolux's intelligent steer-by-wire solution makes cars smarter and safer
- 8051 MCU - Parity Check
- How to efficiently balance the sensitivity of tactile sensing interfaces
- What should I do if the servo motor shakes? What causes the servo motor to shake quickly?
- 【Brushless Motor】Analysis of three-phase BLDC motor and sharing of two popular development boards
- Midea Industrial Technology's subsidiaries Clou Electronics and Hekang New Energy jointly appeared at the Munich Battery Energy Storage Exhibition and Solar Energy Exhibition
- Guoxin Sichen | Application of ferroelectric memory PB85RS2MC in power battery management, with a capacity of 2M
- Analysis of common faults of frequency converter
- In a head-on competition with Qualcomm, what kind of cockpit products has Intel come up with?
- Dalian Rongke's all-vanadium liquid flow battery energy storage equipment industrialization project has entered the sprint stage before production
- Allegro MicroSystems Introduces Advanced Magnetic and Inductive Position Sensing Solutions at Electronica 2024
- Car key in the left hand, liveness detection radar in the right hand, UWB is imperative for cars!
- After a decade of rapid development, domestic CIS has entered the market
- Aegis Dagger Battery + Thor EM-i Super Hybrid, Geely New Energy has thrown out two "king bombs"
- A brief discussion on functional safety - fault, error, and failure
- In the smart car 2.0 cycle, these core industry chains are facing major opportunities!
- The United States and Japan are developing new batteries. CATL faces challenges? How should China's new energy battery industry respond?
- Murata launches high-precision 6-axis inertial sensor for automobiles
- Ford patents pre-charge alarm to help save costs and respond to emergencies
- New real-time microcontroller system from Texas Instruments enables smarter processing in automotive and industrial applications
- Tesla's electric motor
- Design of prison security system by integrating wireless sensors with control network
- Fast charging knowledge sharing: PD protocol fast charging
- [Voice Recognition Positioning] Material Unboxing-ESP32-S2-KALUGA-1
- EEWORLD University ---- The latest version of RTOS training - 15 days to get started with RT-Thread kernel
- [Engineer's Notes] Use 4 "attentions" in PCB wiring to avoid surges!
- EEWORLD University ----3
- What development environment is used for bare metal programming of imax6ull
- SparkRoad serial port to localbus to achieve command control
- EEWORLD University Hall----Live Replay: STMicroelectronics SiC Products and Industrial Application Guide



 HA5351IBZ
HA5351IBZ











 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号