|
1967 views|1 replies
alan000345
Currently offline
|
The OP
Published on 2021-4-26 09:43
Only look at the author
This post is from RF/Wirelessly
Latest reply
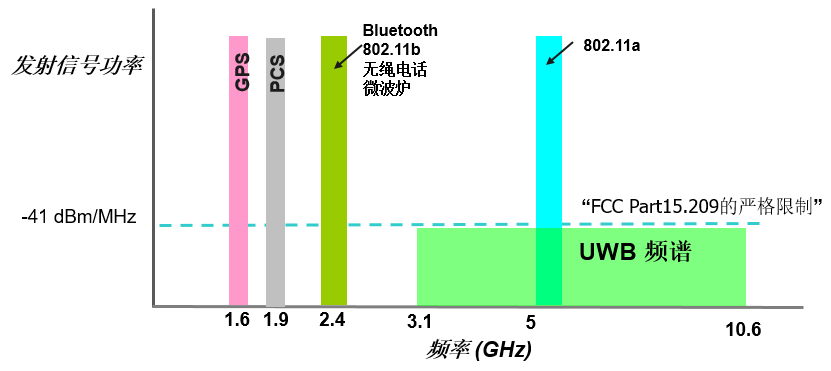
UWB is an ultra-wideband signal with a very long range!
Details
Published on 2021-4-26 11:10
| |
|
|
||
|
w494143467
Currently offline
|
2
Published on 2021-4-26 11:10
Only look at the author
|
|
|
|
|
|
- 【Posts】What exactly is UWB technology?
- 【Posts】What exactly is the UWB "One-Finger Connection" technology released by Xiaomi? What is its use?
- 【Posts】What does this orientation of the current clamp mean?
- 【Posts】What exactly is embedded software?
- 【Posts】TI enters the M0 MCU camp. What is it up to?
- 【Posts】Which parameters in the BUCK circuit are determined by the inductance value?
- 【Posts】What is the purpose of connecting two PMOS in series?
- 【Posts】The most detailed summary of embedded system knowledge and interface technology ever!
- 【Download】I have no idea what it is, please research it yourself!
- 【Download】Research on high-precision indoor three-dimensional positioning technology based on UWB_Chen Yan
- 【Download】With the rapid development of information technology, the development trend of UWB personnel positioning is immeasurable
- 【Download】Introduction to UWB Ultra-Wideband Technology
- 【Download】TI MSP430FR5969 design practice strategy - to carry out low power design to the end!
- 【Download】PCB full set of technical information
- 【Download】Analog Electronic Technology Basic Courseware (Huachengying) Classic.pdf
- 【Download】IGBT module technology driver and application
- 【Design】UWB positioning driving car
- 【Design】UWB Base Station Module
- 【Design】#The 4th LiChuang Competition# Indoor positioning demonstration system based on UWB
- 【Design】Trimension? SR040 UWB module with built-in antenna: ASMOP1CO0A1
- 【Design】Trimension? SR040 UWB module with built-in RF connector: ASMOP1CO0R1
- 【Design】Trimension? UWB Development Kit
- 【Circuits】What is a power distribution system and what exactly does power integrity mean?
- 【Circuits】How many types of power supplies are there?
- 【Circuits】How to judge the quality of LED power supply?
- 【Circuits】ToF high-performance development platform, what are the implementation scenarios of ADI innovative applications?
- 【Circuits】What are chip multilayer ceramic capacitors?
- 【Circuits】What are the hot spots in integrated circuit research?
- 【Articles】NIO upgrades its central computing platform. What exactly is cabin-driving integration technology?
- 【Articles】DLP, ISC? What are these headlight technologies?
- 【Articles】Smart speakers: a blue ocean or a pitfall? What are the key technologies?
- 【Articles】What is the charm of Quanji Technology's UWB digital key?
- 【Articles】What exactly are sbit and sfr?
- 【Articles】What is PLC motion control? Differences between PLC interpolation and synchronous interpolation
-
What exactly is the UWB \"One-Finger Connection\" technology released by Xiaomi? What is its use?
Xiaomihasofficiallylaunchedanewtechnology,"One-fingerconnection"UWB,claimingthatitwillgivemobilephonesandsmartdevicestheabilityof"spatialperception",whichcanachievethepurposeofdirectionalcontrolbypointingthemobilephoneatthedeviceWhatisitand ...
-
What does this orientation of the current clamp mean?
TodayIsawapinpointcurrentclamp,whichwasmarkedwiththedirectionofthearrowtoclampthecurrentcabletobemeasuredHowever,forsinusoidalAC,thereisnopositiveornegative,orthepositiveandnegativechangeatanytimeNotonlyisthereadirectionmarkingonthecurrentc ...
-
Is there a common anode digital tube with the same package as ARK SR420361K?
Iwouldliketoasktheexperts,isthereacommonanodedigitaltubewiththesamepackageasARKSR420361K?Thankyou
- Bluetooth module parameters - transmit power, receive sensitivity, air rate, what equipment can be used to test these parameters more accurately...
- The headlight step-down chip already has a DIM enable terminal to control the on and off of the headlights, so why add a circuit to control the BAT+ supply...
- E-book "The Beauty of Mathematics" 2nd Edition
- Analysis of ZigBee Terminal Direct Join Method
- 【Running posture training shoes】No.008-Android APP design
- EEWORLD University Hall----Mentor PADS VX2 four-layer router
- High-speed universal PCI serial port card
EEWorld Datasheet Technical Support
-
"Cross-chip" quantum entanglement helps build more powerful quantum computing capabilities
IBM scientists have achieved "cross-chip" quantum entanglement - successfully entangled two "Eagl
-
Ultrasound patch can continuously and noninvasively monitor blood pressure
A research team at the University of California, San Diego, has developed an innovative wearable
-
Europe's three largest chip giants re-examine their supply chains
At the Electronica 2024 CEO Roundtable held just last week, the CEOs of three chip giants, Infine
- It is reported that Kioxia will be approved for listing as early as tomorrow, and its market value is expected to reach 750 billion yen
- The US government finalizes a $1.5 billion CHIPS Act subsidy to GlobalFoundries to support the latter's expansion of production capacity in the US
- SK Hynix announces mass production of the world's highest 321-layer 1Tb TLC 4D NAND flash memory, plans to ship it in the first half of 2025
- UWB is a new way to use it in cars. Can wireless BMS also use it?
- Filling the domestic gap! China Mobile, Huawei and others jointly released the first GSE DPU chip
- Samsung Electronics NRD-K Semiconductor R&D Complex to import ASML High NA EUV lithography equipment
- Apple reveals the secret of its own chip success: competitors can't use the latest cutting-edge technology
- Problems with STM32 and passive buzzer playing sound
- Embedded Tutorial_DSP Technology_DSP Experiment Box Operation Tutorial: 2-28 Building a Lightweight WEB Server Experiment
- OPA847IDBVR op amp domestic replacement
- AG32VF407 Test UART
- [Digi-Key Follow Me Issue 2] Chapter 1: Sharing on receiving the goods
- What model is this infrared receiver? Which model can be used instead? Thank you
- Selling brand new unopened ZYNQ 7Z020 FPGA core board
- The LORA module used in the lithium battery-powered water meter setting can save energy when 100 water meters are installed in one corridor.
- I would like to ask, when a port is set to RX0, is it necessary to set the input and output direction of this port?
- Why is this year so difficult? It’s even more difficult than during the pandemic. I’m 30 and facing unemployment. I’m so confused.
- Ask about the voltage regulator test question
- [Xiaohua HC32F448 Review] About Xiaohua Semiconductor's UART interrupt sending and PRINTF construction and redirection
- 【BIGTREETECH PI development board】 HDMI output test
- 【BIGTREETECH PI development board】+08. Audio test (zmj)
- [Xiaohua HC32F448 Review] +RTC electronic clock


 提升卡
提升卡 变色卡
变色卡 千斤顶
千斤顶