|
The OP
Published on 2019-8-8 21:26
Only look at the author
This post is from RF/Wirelessly
| ||
|
|
||
- 【Posts】Reference design of a true wireless headset charging box with ultra-low standby power consumption
- 【Posts】Wireless Earbud Battery Ultra-Low Standby Power Consumption Reference Design
- 【Posts】Ultra-low standby power consumption < 90mW non-auxiliary AC/DC power supply reference design
- 【Posts】Detailed explanation of the BQ25618/9 dedicated switch charging chip for TWS true wireless headset charging compartment
- 【Posts】Wireless charging solution "XS016 fully integrated MCU + micro IPM architecture"
- 【Posts】Are you interested in DIYing a USB charger?
- 【Posts】PD decoy XSP01 is successfully made, supports PD3.0 fast charging protocol, and is tested with iPhone 18W charging head
- 【Posts】What domestic chips are needed to DIY a fast-charging chromium iron or an electric chromium iron that works as a laptop power supply?
- 【Download】High efficiency and ultra-low standby power consumption mobile phone charger based on AP3768
- 【Download】Design of a low standby power switching power supply charger
- 【Download】Design of microcontroller power supply based on ultra-low voltage charge pump
- 【Download】6.6kw charger reference design introduction
- 【Download】1 to 4 Cell Li-Ion Battery SMBus Charge Controller Reference Design Schematic
- 【Download】High Efficiency Synchronous Switch-Mode Charger Controller Reference Design Schematic for Solar Cell Charging
- 【Download】Automotive USB Battery Charging Reference Design Files
- 【Download】1 to 4 Cell Li-Ion Battery SMBus Charge Controller Reference Design BOM
- 【Design】Ultra-low standby power less than 90mW auxiliary AC/DC power supply reference design
- 【Design】Wireless earbud battery ultra-low standby power reference design
- 【Design】10 yuan ultra-low-cost portable adjustable power supply (18650 battery) (can be used as a power bank)
- 【Design】High-Efficiency 65W USB-C Dual-Port Charger Reference Design with ATQ Transformer
- 【Design】100W USB-C dual-port charger reference design with single-stage PFC
- 【Design】170 W AC-DC reference design with input voltage range for e-bike and power tool battery chargers
- 【Circuits】MAX1555 reference design circuit | battery charger application circuit
- 【Circuits】Electric vehicle battery charging protection circuit
- 【Circuits】Fabrication of multi-cell lithium battery charging circuit
- 【Circuits】A simple circuit diagram of abnormal mobile phone charging alarm
- 【Circuits】A simple and easy-to-make rechargeable hypnotist
- 【Circuits】Simple and practical battery automatic charging protection device
- 【Articles】Application of AP3765 in ultra-low standby power consumption charger solution
- 【Articles】High efficiency and ultra-low standby power consumption mobile phone charger based on AP3768
- 【Articles】Mobile phone charger solution that meets 30mW standby power consumption requirement
- 【Articles】Design of a mobile phone charger with a standby power consumption of only 30mW
- 【Articles】Low standby power consumption mobile phone charger power management IC application
- 【Articles】Practical mobile phone charger solution that meets 30mW standby power requirement
-
Ultra-low standby power consumption < 90mW non-auxiliary AC/DC power supply reference design
[size=4]Ultra-lowstandbypowerconsumptionoflessthan90mWwithoutauxiliaryAC/DCpowersupplyreferencedesignDCMPFCcontroller,UCC256304enhancedLLCcontrollerandintegrateddrivertoprovide12V/104Apeakcurrent)fromuniversalACinput4%peakefficiencyat115VAC ...
-
Wireless Earbud Battery Ultra-Low Standby Power Consumption Reference Design
Newwirelessearbudsarechargedfromabatteryinsidethecarryingcase-ThisuniquedesignrequiresasmallsolutionsizeandefficientpowercomponentsThisultra-lowpowerreferencedesignshowcasesthechargingcasebatteryandboostconverterpoweredbyaUSBinput.18-μAult ...
-
Understanding the boost small signal model
Helloeveryone!I'mlearningaboutBoostsmallsignalmodelingrecentlyCouldyoupleasehelpexplainthemeaningofthefollowingsmallsignalmodel?Thankyou!
- Which of these five books do you want to be online first? Come and vote for it~
- Allwinner T113 dual-core heterogeneous processor based on Tina Linux5.0 - RTOS system custom development
- Power amplifier circuit learning
- [Lazy self-care fish tank control system] APP control pins in non-RTE mode of KEIL environment
- A large collection of classic IoT resources, which are being continuously updated. Please pay attention!
- Application of machine vision inspection in electronic connector manufacturing industry
- POE power supply problem
EEWorld Datasheet Technical Support
-
Europe's three largest chip giants re-examine their supply chains
At the Electronica 2024 CEO Roundtable held just last week, the CEOs of three chip giants, Infine
-
It is reported that Kioxia will be approved for listing as early as tomorrow, and its market value is expected to reach 750 billion yen
On November 21, Reuters reported that with the support of Bain Capital, Kioxia will obtain approv
-
The US government finalizes a $1.5 billion CHIPS Act subsidy to GlobalFoundries to support the latter's expansion of production capacity in the US
On November 21, the U.S. Department of Commerce officially announced yesterday that it will provi
- SK Hynix announces mass production of the world's highest 321-layer 1Tb TLC 4D NAND flash memory, plans to ship it in the first half of 2025
- UWB is a new way to use it in cars. Can wireless BMS also use it?
- Filling the domestic gap! China Mobile, Huawei and others jointly released the first GSE DPU chip
- Samsung Electronics NRD-K Semiconductor R&D Complex to import ASML High NA EUV lithography equipment
- Apple reveals the secret of its own chip success: competitors can't use the latest cutting-edge technology
- A big chip war is about to start: Qualcomm and MediaTek are involved in notebooks, and AMD is reported to enter the mobile phone market
- Exynos 2600 chip is the key, Samsung is reportedly going to launch a 2nm chip counterattack
- Problems with STM32 and passive buzzer playing sound
- Embedded Tutorial_DSP Technology_DSP Experiment Box Operation Tutorial: 2-28 Building a Lightweight WEB Server Experiment
- OPA847IDBVR op amp domestic replacement
- AG32VF407 Test UART
- [Digi-Key Follow Me Issue 2] Chapter 1: Sharing on receiving the goods
- What model is this infrared receiver? Which model can be used instead? Thank you
- Selling brand new unopened ZYNQ 7Z020 FPGA core board
- The LORA module used in the lithium battery-powered water meter setting can save energy when 100 water meters are installed in one corridor.
- I would like to ask, when a port is set to RX0, is it necessary to set the input and output direction of this port?
- Why is this year so difficult? It’s even more difficult than during the pandemic. I’m 30 and facing unemployment. I’m so confused.
- Ask about the voltage regulator test question
- [Xiaohua HC32F448 Review] About Xiaohua Semiconductor's UART interrupt sending and PRINTF construction and redirection
- 【BIGTREETECH PI development board】 HDMI output test
- 【BIGTREETECH PI development board】+08. Audio test (zmj)
- [Xiaohua HC32F448 Review] +RTC electronic clock



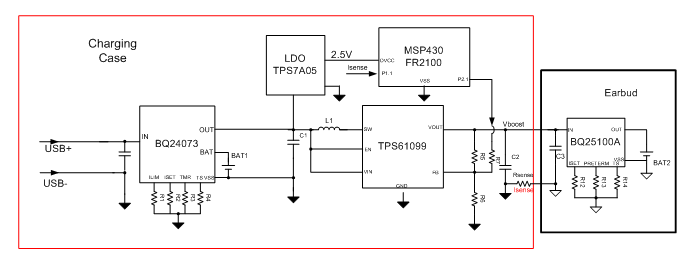
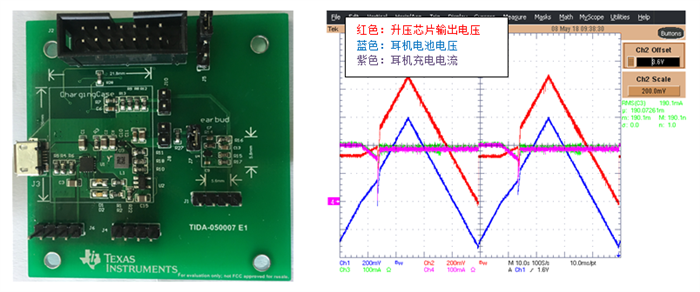
 提升卡
提升卡 变色卡
变色卡 千斤顶
千斤顶