USB interface circuit design of FT245BM and FPGA
Source: InternetPublisher:红水杯 Keywords: Power supply other power circuits Updated: 2020/04/01
The USB bus is favored by developers due to its many advantages such as fast transmission speed, low resource consumption, and true plug-and-play, and has become a basic configuration of many computer equipment. There are currently two widely used USB device development solutions: (1) Using the USB device end interface chip plus a microcontroller structure. For example, PDIUSBD12/ISP1581 of Philips Company, which is widely used in China. (2)Using USB microcontroller. Using these two solutions requires developers to thoroughly understand the details of the USB protocol and write firmware programs. The operation of the firmware takes up the time and space resources of the microcontroller, and the actual communication efficiency is not very high. Some people also use FPGA to implement firmware functions, but this solution is very difficult to develop and debug. In actual work, I directly connect a USB protocol chip FT245BM externally to the FPGA to realize USB communication between the FPGA and the PC. This method does not require a microcontroller, reduces the number of components, and takes up very little FPGA resources. The FPGA is still Other logical functions can be implemented, and the system design has great flexibility.
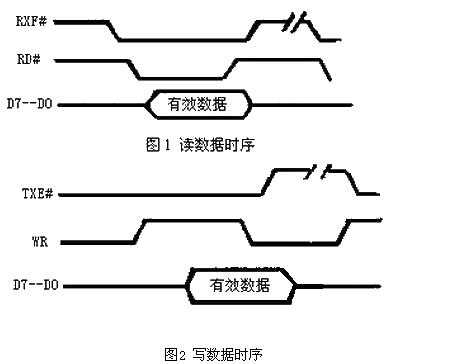
For the internal structure and detailed pin introduction of FT245BM, readers can refer to other relevant materials. Here we only give an introduction to the content related to this design. FT245BM contains two FIFO data buffers, one is a 128-byte receive buffer and the other is a 384-byte send buffer. They are used as exchange buffers for USB data and parallel I/O port data. FIFO implements the interface with the outside world (microcontroller, FPGA or other devices), mainly through 8 data lines D0~D7, read and write control lines RD# and WR#, FIFO send buffer empty flag TXE# and FIFO receive buffer The non-null flag RXF is used to complete data exchange. If TXE# is low, it means that the current FIFO send buffer is empty. If it is high, it means that the current FIFO send buffer is full or the previous byte is being stored. Writing data to the buffer is prohibited. RXF# is low indicating that the current FIFO receive buffer is not empty. The RD# signal changes from low to high to read data from the FIFO buffer. Data is sent to the data bus when RD# goes low. Data cannot be read from the FIFO when RXF# is high. See Figure 1 and Figure 2 for the read and write timing.
Interface circuit design between FT245BM and FPGA
Hardware circuit design
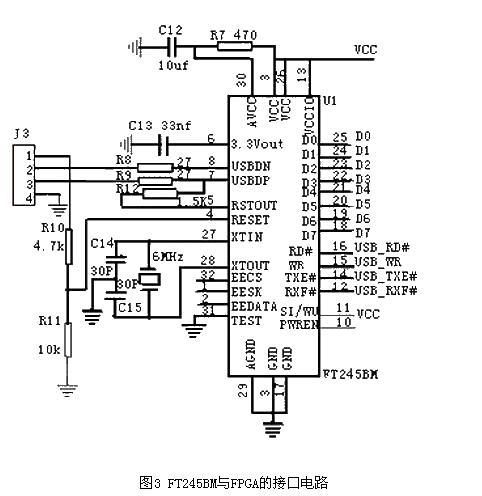
Figure 3 is the interface circuit between the USB and FPGA of FT245BM. The FPGA uses ALTERA EPF1K50TC-144. D0~D7 are the data buses for exchanging data between FT245BM and FPGA. USB_RD#, USB_WR, USB_TXE#, and USB_RXF# are the relevant control buses.
- A very convenient small power supply circuit to share
- How to Make a Soft Latch Circuit
- How to use a simple circuit to achieve a smooth soft-start for an isolated converter
- Basic circuit description of adjustable voltage regulator LM317
- Op amp power supply decoupling bypass measures
- The constant current source composed of two transistors can drive high power
- How to use SBR to improve power conversion efficiency
- Dual forward converter schematic diagram
- Integrated regulated power supply with continuously adjustable output voltage
- Self-made high-stability, high-current, DC adjustable voltage-stabilized power supply using operational amplifier
- Determining the prerequisites for successful circuit board design
- About star-delta step-down start plc ladder diagram circuit diagram
- Photosensitive automatic dimming desk lamp circuit and principle
- Humidity detection circuit schematic diagram
- Two-channel low-power amplifier circuit
- Heart rate detection circuit
- How to use "virtual short" and "virtual break" to analyze op amp circuits
- Unity gain four input audio mixer
- Dual tone generator for audio
- Simple mode logarithmic amplifier circuit of LOG100







 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号