Micromotor pedal speed regulator circuit and improvement
Source: InternetPublisher:国民男神经 Updated: 2021/12/27
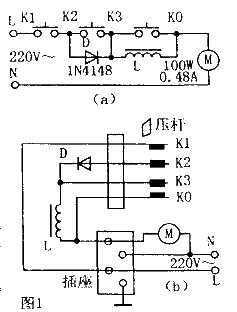
Micromotor pedal speed regulators are often used in small winding machines, sewing machines, hemming machines, etc., as step speed regulators. The speed-regulating motor is generally a single-phase series-excited micromotor with a power of 100W and a current of 0.48A. The electrical schematic diagram of this type of foot speed regulator is shown in Figure 1a. The wiring diagram is shown in Figure 1b. Its working principle is: when the pedal is pressed down to connect K1 and K2, the 220V mains power is connected in series through the diode D and the reactor L and then connected to the micromotor M. Due to the one-way conduction of the diode, the voltage obtained by the micromotor is half The average value of the wave (how many volts the DC voltage drop of L is) is about 95V. The micromotor is running at low speed: when the foot pressure lever turns on K1, K2, and K3 at the same time, D is short-circuited by K2 and K3, and the 220V city The electricity is depressurized by L and then applied to the micromotor. The micromotor is running at a medium speed. When the foot pressure lever turns on K1, K2, K3, and K0, 220V mains power is directly applied to the micromotor. At this time , the micromotor runs at full speed, and the torque is maximum at this time. Usually, the micromotor starts more frequently, and the foot pedal speed regulator bears a larger current, which often causes the speed regulator contacts to melt, stick, and be damaged. And cause damage to the micromotor brushes, armature, etc., causing a lot of inconvenience to the user.
The circuit schematic diagram of the improved foot speed regulator is shown in Figure 2a. The wiring diagram is shown in Figure 2b. The improved foot speed regulator adopts triac AC technology and uses changing the RC phase shift time constant to control the conduction angle of the triac to adjust the voltage applied to the micromotor to adjust the micromotor. speed purpose. The improved speed regulator uses the original switching on and off of K1, K2, and K3 to adjust the RC time constant. Therefore, K1, K2, and K3 bear very little current, which can greatly extend the service life of their contacts and also improve the reliability and service life of the speed regulator. The improved speed regulator still adopts the stepped speed regulation method of low speed, medium speed and full speed, and has the characteristics of easy production, cost saving, reliable performance and extended service life.
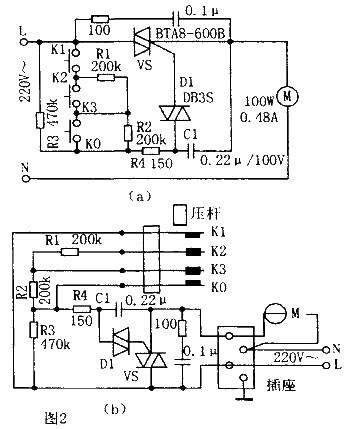
working principle:
Usually when K1, K2 and K3 are in the disconnected state, due to the large resistance of R3, its RC phase shift circuit cannot trigger VS to turn on. When the pedal is pressed down to connect K1 and K2, R1 and R2 are connected to the circuit, and the RC time constant formed by them causes the triac to conduct at a small conduction angle, causing the micromotor to run at low speed. Adjust R1 to get the appropriate low speed. When the foot pressure lever connects K1, K2, and K3, R1 is short-circuited, R=(R2//R3)+R4, the RC time constant is in a moderate state, the conduction angle of the triac is also in a moderate state, and the micro The motor runs at medium speed, and the required medium speed can be obtained by adjusting R2. When the foot pressure lever connects K1, K2, K3, and K0, R1 and R2 are short-circuited. At this time, R=R4, the RC time constant is minimum, and the micromotor runs at full speed. Therefore, by adjusting the on-off of K1, K2, and K3 via the pedal pressure lever, the micromotor can be adjusted to operate at three speeds: low speed, medium speed, and full speed.
The improved speed regulator uses a typical inductive load triac speed regulating circuit, which can effectively prevent the inductance characteristics of the micromotor from affecting the operational reliability of the triac speed regulating circuit. If you need to change to continuous stepless speed regulation, just replace R1 and R2 with a 470kΩ potentiometer. In addition, the foot pressure lever is changed to a sawtooth pressure lever that can drive the gear rotation to drive the potentiometer to rotate and adjust the RC time constant to achieve the purpose of continuous speed regulation.
Selection of components:
D1 uses a bidirectional trigger diode such as DB3S; VS uses a plastic-encapsulated bidirectional thyristor such as BTA8-600B with a withstand voltage of 600V and a current of 8A. Since there are fewer components, insulating brackets can be used to fix the components.
- Making a photometer with light measuring function
- Experiment on realizing photoelectric alarm using photosensitive devices
- Measurement and analysis of automatic emergency lighting circuit
- Musical doorbell without buttons
- Lighting lamp voltage stabilizing circuit (2)
- 4-digit incandescent lamp display circuit
- Remote anti-theft alarm
- Automotive LED driver circuit diagram using LT3486
- Four color light circuit
- Reverse polarity drive circuit
- 555 timer disconnection photoelectric isolation safety protection circuit
- Breathing light circuit diagram designed by NE555
- Micromotor pedal speed regulator circuit and improvement
- The battery fast charging circuit is composed of BQ2002 battery fast charging control integrated circuit
- Use 555 to make DC-DC boost circuit







 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号