|
The OP
Published on 2023-11-21 16:15
Only look at the author
This post is from RF/Wirelessly
Latest reply
It seems that civilians have never seen such equipment.
Details
Published on 2023-11-22 17:59
| ||
|
|
||
|
wangerxian
Currently offline
|
2
Published on 2023-11-21 16:50
Only look at the author
This post is from RF/Wirelessly
Comments | |
|
|
||
|
|
|
3
Published on 2023-11-21 21:02
Only look at the author
This post is from RF/Wirelessly
Comments
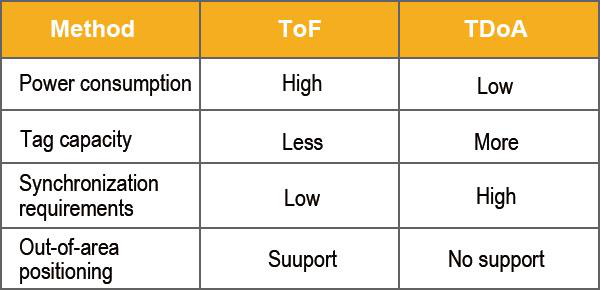
TDOA technology currently exists, but it has very high requirements for time synchronization (us level), so it is difficult to build.
Details
Published on 2023-11-22 09:16
| ||||||||||
|
Personal signature
玩板看这里: https://bbs.eeworld.com.cn/elecplay.html EEWorld测评频道众多好板等你来玩,还可以来频道许愿树许愿说说你想要玩的板子,我们都在努力为大家实现! |
||||||||||
|
|
|
4
Published on 2023-11-22 08:41
Only look at the author
This post is from RF/Wirelessly
Comments
Yes, the cost is not high. Two modules should cost less than two hundred yuan, and you can play with ranging. If you want to play with positioning, four modules can be used.
Details
Published on 2023-11-22 09:17
| ||
|
|
||
|
|
|
wangerxian
Currently offline
|
5
Published on 2023-11-22 09:16
Only look at the author
This post is from RF/Wirelessly
| |
|
|
||
|
|
|
wangerxian
Currently offline
|
6
Published on 2023-11-22 09:17
Only look at the author
This post is from RF/Wirelessly
Comments | |
|
|
||
|
|
|
7
Published on 2023-11-22 10:52
Only look at the author
This post is from RF/Wirelessly
Comments
Yes, our previous search and rescue equipment has used this technology to locate the position of rescuers.
Details
Published on 2023-11-22 13:40
| ||
|
|
||
|
|
|
wangerxian
Currently offline
|
8
Published on 2023-11-22 13:40
Only look at the author
This post is from RF/Wirelessly
Comments | |
|
|
||
|
|
|
9
Published on 2023-11-22 15:09
Only look at the author
This post is from RF/Wirelessly
Comments
Yes, that device is called a locator, and the technology integrated in it is amazing.
Details
Published on 2023-11-22 17:58
| ||||||||||
|
Personal signature
玩板看这里: https://bbs.eeworld.com.cn/elecplay.html EEWorld测评频道众多好板等你来玩,还可以来频道许愿树许愿说说你想要玩的板子,我们都在努力为大家实现! |
||||||||||
|
|
|
10
Published on 2023-11-22 15:51
Only look at the author
This post is from RF/Wirelessly
Comments
It seems that civilians have never seen such equipment.
Details
Published on 2023-11-22 17:59
| ||
|
|
||
|
|
|
wangerxian
Currently offline
|
11
Published on 2023-11-22 17:58
Only look at the author
This post is from RF/Wirelessly
| |
|
|
||
|
|
|
wangerxian
Currently offline
|
12
Published on 2023-11-22 17:59
Only look at the author
This post is from RF/Wirelessly
| |
|
|
||
|
|
- 【Posts】Comparison of UWB positioning technologies: TOF & TDOA
- 【Posts】This article will show you what UWB triangulation positioning, TDoA and PDoA positioning are
- 【Posts】UWB Ranging TOA and TDOA Detailed Explanation
- 【Posts】UWB Indoor Positioning Technology
- 【Posts】[X-NUCLEO-53L4A3 TOF evaluation board] Unboxing experience and conventional distance measurement
- 【Posts】Comparison of UWB positioning technologies: TOF & TDOA
- 【Posts】What is the dynamic voltage positioning technology here?
- 【Posts】I plan to share some UWB technology. Can you give me some suggestions?
- 【Download】TDOA positioning technology based on genetic algorithm and simulated annealing algorithm
- 【Download】Supports TDOA algorithm positioning UWB positioning badge work card tag DW1000 solution with SOS button VDU1501
- 【Download】10cm positioning accuracy UWB base station_using DW1000 solution_TDOA indoor positioning algorithm VDU2501 datasheet
- 【Download】Research on high-precision indoor three-dimensional positioning technology based on UWB_Chen Yan
- 【Design】UWB positioning driving car
- 【Design】UWB Base Station Module
- 【Design】#The 4th LiChuang Competition# Indoor positioning demonstration system based on UWB
- 【Design】Trimension? SR040 UWB module with built-in antenna: ASMOP1CO0A1
- 【Design】Trimension? SR040 UWB module with built-in RF connector: ASMOP1CO0R1
- 【Design】Trimension? UWB Development Kit
- 【Circuits】ToF high-performance development platform, what are the implementation scenarios of ADI innovative applications?
- 【Articles】Xiaomi invented a solution for finding cars in garages based on UWB positioning technology
- 【Articles】Apple and Samsung have entered the UWB positioning technology market. How long should domestic manufacturers wait?
- 【Articles】New Indoor Positioning Technology: Ultra-Wideband (UWB)
- 【Articles】Positioning technology of UWB-based wireless sensor networks
-
This article will show you what UWB triangulation positioning, TDoA and PDoA positioning are
Withthecontinuousadvancementofwirelesstechnology,people'sdemandforpositioningtechnologyisalsoincreasingAlthoughtraditionalpositioningtechnologyhasmadegreatprogress,insomespecificscenarios,therearestillproblemssuchaslowaccuracyandsusceptibil ...
-
UWB Ranging TOA and TDOA Detailed Explanation
[size=4]TOAstandsfor"timeofarrival"size][align=center][attach]394755[/attach][/align][size=4]1[/size][size=4]2[/size][size=4]3[/size][size=4]4[/size][size=4]d=c2wherecisthespeedoflightsize][size=4]Ofcourse,inordertobemorereliableinactualapp ...
-
Help! My newly bought power bank is broken!
Help,help!Thenewlyboughtpowerbankhas5V2AinputandmultipleoutputportsAfteralongtime,hefoundthatthepowerremainedat68%BecauseitwasmyfirsttimeusingitOrdidmyhusbandbreakit
- I have a question about the network port circuit?
- [X-NUCLEO-53L4A3 TOF evaluation board] 4. Simple accuracy test comparison of different targets
- Altiumdesigner 09 import Gerber file with fewer layers
- Which companies are doing well in domestic low-power MCUs?
- MSP430F1232 interrupt learning
- [Discussion] Resistance measurement circuit and judgment circuit
- How to calculate power line width and overcurrent
EEWorld Datasheet Technical Support
-
"Cross-chip" quantum entanglement helps build more powerful quantum computing capabilities
IBM scientists have achieved "cross-chip" quantum entanglement - successfully entangled two "Eagl
-
Ultrasound patch can continuously and noninvasively monitor blood pressure
A research team at the University of California, San Diego, has developed an innovative wearable
-
Europe's three largest chip giants re-examine their supply chains
At the Electronica 2024 CEO Roundtable held just last week, the CEOs of three chip giants, Infine
- It is reported that Kioxia will be approved for listing as early as tomorrow, and its market value is expected to reach 750 billion yen
- The US government finalizes a $1.5 billion CHIPS Act subsidy to GlobalFoundries to support the latter's expansion of production capacity in the US
- SK Hynix announces mass production of the world's highest 321-layer 1Tb TLC 4D NAND flash memory, plans to ship it in the first half of 2025
- UWB is a new way to use it in cars. Can wireless BMS also use it?
- Filling the domestic gap! China Mobile, Huawei and others jointly released the first GSE DPU chip
- Samsung Electronics NRD-K Semiconductor R&D Complex to import ASML High NA EUV lithography equipment
- Apple reveals the secret of its own chip success: competitors can't use the latest cutting-edge technology
- Problems with STM32 and passive buzzer playing sound
- Embedded Tutorial_DSP Technology_DSP Experiment Box Operation Tutorial: 2-28 Building a Lightweight WEB Server Experiment
- OPA847IDBVR op amp domestic replacement
- AG32VF407 Test UART
- [Digi-Key Follow Me Issue 2] Chapter 1: Sharing on receiving the goods
- What model is this infrared receiver? Which model can be used instead? Thank you
- Selling brand new unopened ZYNQ 7Z020 FPGA core board
- The LORA module used in the lithium battery-powered water meter setting can save energy when 100 water meters are installed in one corridor.
- I would like to ask, when a port is set to RX0, is it necessary to set the input and output direction of this port?
- Why is this year so difficult? It’s even more difficult than during the pandemic. I’m 30 and facing unemployment. I’m so confused.
- Ask about the voltage regulator test question
- [Xiaohua HC32F448 Review] About Xiaohua Semiconductor's UART interrupt sending and PRINTF construction and redirection
- 【BIGTREETECH PI development board】 HDMI output test
- 【BIGTREETECH PI development board】+08. Audio test (zmj)
- [Xiaohua HC32F448 Review] +RTC electronic clock



 提升卡
提升卡 变色卡
变色卡 千斤顶
千斤顶



