The constant voltage method[1] for measuring high resistance requires an instrument capable of measuring low currents and a DC constant voltage source. Some electrometers and picoammeters[2] have built-in voltage sources that automatically calculate the unknown resistance. The
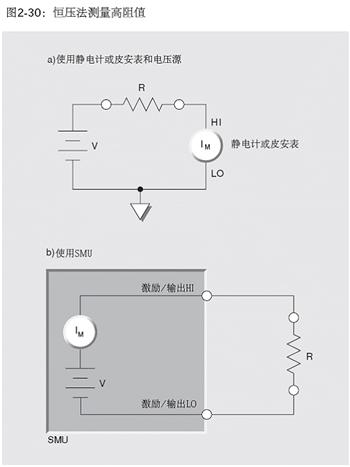
basic circuit configuration for the constant voltage method using an electrometer and picoammeter is shown in Figure 2-30a. Figure 2-30b shows the constant voltage method for high resistance measurements using an SMU[3].
In this method, a constant voltage source (V) is connected in series with the unknown resistance (R) and an ammeter (IM). Since the voltage drop across the ammeter is negligible, all of the test voltage appears across the resistor R. The resulting current is measured by the ammeter, and the resistance is calculated using Ohm's law (R = V/I).
High resistance is usually a function of applied voltage, so the constant voltage method is superior to the constant current method. By measuring at a selected voltage, a resistance vs. voltage curve can be obtained, and the "voltage coefficient of resistance" can be determined.
Applications using this method include testing two-terminal high resistance devices, measuring insulation resistance, and determining the bulk and surface resistivity of insulating materials.
The constant voltage method requires measuring low currents, so the various techniques and error sources described in Section 2.3 (low current measurements [4]) apply to this method. The two most common sources of error when measuring high resistances are electrostatic interference and leakage current. Shielding high impedance circuits can minimize the effects of electrostatic interference, as described in Section 2.6.2. The effects of leakage current can be controlled using the protection techniques described in Section 2.3.1.
Reference address:How does an electrometer measure high resistance greater than 1GΩ using the constant voltage method?
basic circuit configuration for the constant voltage method using an electrometer and picoammeter is shown in Figure 2-30a. Figure 2-30b shows the constant voltage method for high resistance measurements using an SMU[3].
In this method, a constant voltage source (V) is connected in series with the unknown resistance (R) and an ammeter (IM). Since the voltage drop across the ammeter is negligible, all of the test voltage appears across the resistor R. The resulting current is measured by the ammeter, and the resistance is calculated using Ohm's law (R = V/I).
High resistance is usually a function of applied voltage, so the constant voltage method is superior to the constant current method. By measuring at a selected voltage, a resistance vs. voltage curve can be obtained, and the "voltage coefficient of resistance" can be determined.
Applications using this method include testing two-terminal high resistance devices, measuring insulation resistance, and determining the bulk and surface resistivity of insulating materials.
The constant voltage method requires measuring low currents, so the various techniques and error sources described in Section 2.3 (low current measurements [4]) apply to this method. The two most common sources of error when measuring high resistances are electrostatic interference and leakage current. Shielding high impedance circuits can minimize the effects of electrostatic interference, as described in Section 2.6.2. The effects of leakage current can be controlled using the protection techniques described in Section 2.3.1.

Previous article:Basic knowledge of high brightness LED testing
Next article:Insulation resistance test of inductor chips in automotive motors
- Popular Resources
- Popular amplifiers
Latest Test Measurement Articles
- New IsoVu™ Isolated Current Probes: Bringing a New Dimension to Current Measurements
- Modern manufacturing strategies drive continuous improvement in ICT online testing
- Methods for Correlation of Contact and Non-Contact Measurements
- Keysight Technologies Helps Samsung Electronics Successfully Validate FiRa® 2.0 Safe Distance Measurement Test Case
- From probes to power supplies, Tektronix is leading the way in comprehensive innovation in power electronics testing
- Seizing the Opportunities in the Chinese Application Market: NI's Challenges and Answers
- Tektronix Launches Breakthrough Power Measurement Tools to Accelerate Innovation as Global Electrification Accelerates
- Not all oscilloscopes are created equal: Why ADCs and low noise floor matter
- Enable TekHSI high-speed interface function to accelerate the remote transmission of waveform data
MoreSelected Circuit Diagrams
MorePopular Articles
- Intel promotes AI with multi-dimensional efforts in technology, application, and ecology
- ChinaJoy Qualcomm Snapdragon Theme Pavilion takes you to experience the new changes in digital entertainment in the 5G era
- Infineon's latest generation IGBT technology platform enables precise control of speed and position
- Two test methods for LED lighting life
- Don't Let Lightning Induced Surges Scare You
- Application of brushless motor controller ML4425/4426
- Easy identification of LED power supply quality
- World's first integrated photovoltaic solar system completed in Israel
- Sliding window mean filter for avr microcontroller AD conversion
- What does call mean in the detailed explanation of ABB robot programming instructions?
MoreDaily News
- STMicroelectronics discloses its 2027-2028 financial model and path to achieve its 2030 goals
- 2024 China Automotive Charging and Battery Swapping Ecosystem Conference held in Taiyuan
- State-owned enterprises team up to invest in solid-state battery giant
- The evolution of electronic and electrical architecture is accelerating
- The first! National Automotive Chip Quality Inspection Center established
- BYD releases self-developed automotive chip using 4nm process, with a running score of up to 1.15 million
- GEODNET launches GEO-PULSE, a car GPS navigation device
- Should Chinese car companies develop their own high-computing chips?
- Infineon and Siemens combine embedded automotive software platform with microcontrollers to provide the necessary functions for next-generation SDVs
- Continental launches invisible biometric sensor display to monitor passengers' vital signs
Guess you like
- A detailed capacitor sample
- How to reduce 60V to 42V using LM34927
- Detailed explanation of STM32 minimum system circuit
- This online circuit simulation tool YYDS
- Opening: Forever LED Light
- Announcement of Moderator Chip Coin and Physical Gift Rewards in October 2018
- Showing goods + Embedded Primary Development Board (MOOC) video
- ADC12 Register Description
- Altium Designer v20.1.12.249
- EEWORLD University ---- TI-RSLK Module 10 - Debugging Real-time Systems

 Signal Integrity and Power Integrity Analysis (Eric Bogatin)
Signal Integrity and Power Integrity Analysis (Eric Bogatin) 開關電源專業英語
開關電源專業英語











 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号