Motherboards have always been a major hub for high-speed serial buses, and a battleground for high-end oscilloscope manufacturers. However, general users rarely pay attention to the technology behind them, and even computer enthusiasts rarely have a deep understanding of these high-speed serial buses. This article attempts to start with today's top chipsets and briefly explain the high-speed buses on these chipsets and the test equipment to be used.
1 X58
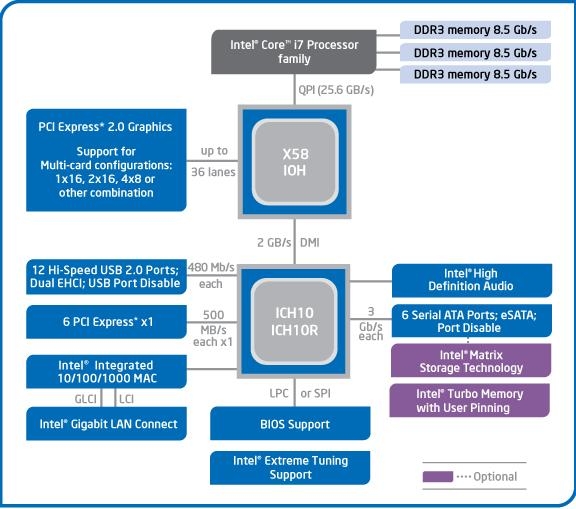
Intel's X58 chipset is the most advanced chipset on PC today, and is also the only chipset that supports Intel I7 CPU. In addition to integrating the most common high-speed serial bus, this chipset also has a major feature: it supports Intel's own QPI bus. The biggest difference between I7 and Intel's previous CPUs is that it integrates a memory controller like AMD K8 and supports 3-channel DDR3 memory. X58 supports 36-Lane PCIE G2, CroosFire, and can directly support SLI through NVIDIA's authorization. Let's take a look at the test requirements of these high-speed serial buses.
QPI
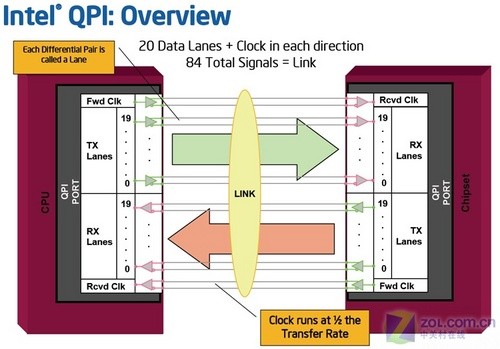
Intel's Quick Path Interface was first introduced on the I7 CPU, using peer-to-peer transmission similar to PCIE, replacing the previous parallel FSB. There are two bit rates for QPI: 4.8Gbps and 6.4Gbps. For 6.4Gbps QPI, when 32bit transmission is used, the bandwidth can reach 25.6GB/s. Compared to the 1600MHz FSB bandwidth of 12.8GB/s, the bandwidth has doubled. It is also better than AMD's HT 3.0 with a bit rate of 5.2Gbps and a bandwidth of 20.8GB/s when transmitting 32bit. At the same time, QPI can not only be used for the interconnection between the CPU and the north bridge chip, but also for the internal interconnection between multi-core processors and the interconnection with the memory controller.
Since the fundamental wave of QPI 6.4Gbps is 3.2GHz, the 1.8bit rate is 11.52GHz, and the 5th harmonic is 16GHz, an oscilloscope with a bandwidth of 16GHz is required for testing. Tektronix and LeCroy both have oscilloscopes with bandwidths above 16GHz, but LeCroy currently has no QPI test solution. Tektronix is the first company in the industry to launch an oscilloscope-based QPI test solution, while Agilent has launched the bit error rate tester J-BERT N4903B.
PCI Express 2.0
PCIE G2 has a bit rate of 5Gbps, a fundamental frequency of 2.5GHz, a 1.8x bit rate of 9GHz, and a 5th harmonic of 12.5GHz. Except for Agilent DSO91304, which has a bandwidth of only 13GHz, which just meets the requirement of the 5th harmonic, Tektronix and LeCroy both have oscilloscopes with bandwidths above 12.5GHz, and Tektronix's oscilloscopes are more popular among board manufacturers.
SATA 3Gbps
SATA 3Gbps, commonly known as SATA 2, has a fundamental frequency of 1.5GHz, a 1.8x bit rate of 5.4GHz, and a 5th harmonic of 7.5GHz. It requires an oscilloscope with a bandwidth of 8GHz, which can be met by Agilent, Tekronix, and LeCroy.
DDR3
DDR3 starts at 800MHz, and the highest that meets the specification is 1600MHz. X58 supports DDR3-1066 with a bandwidth of 8.5GB/S, a bit rate of 1.066Gbps, a fundamental wave of 533MHz, a 1.8x bit rate of 1.9188GHz, and a fifth harmonic of 2665. Agilent and Tektronix have both launched DDR3 test solutions.
USB 2.0 High SpeedUSB 2.0 can be said to be the entry-level high-speed serial bus, with a bit rate of only 480Mbps, a fundamental wave of 240MHz, a 1.8x bit rate of 864MHz, and a fifth harmonic of 1.2GHz. In fact, the USB certification organization believes that an oscilloscope with a bandwidth of 1GHz can meet the consistency test of USB2.0 High Speed.
In addition, the DMI bus between X58 and ICH10 is based on PCIE G2 x4, with a bandwidth of 2GB/s, which is similar to AMD's A-link interconnection between the north and south bridges (also based on PCIE G2 X4).
2. RD790FX
Compared with x58, AMD's competing product is RD790, and the most advanced one is RD790FX. 790FX natively supports 40 Lane PCIE G2, of which 32 lanes are allocated to graphics cards to form 2x16 and 4x8 crossfire, 6 lanes are allocated to peripherals, and the other 4 lanes form Alink to connect the north and south bridges.
The difference from X58 is that the CPU and RD790FX are connected via HT 3.0, and the memory only supports DDR2.
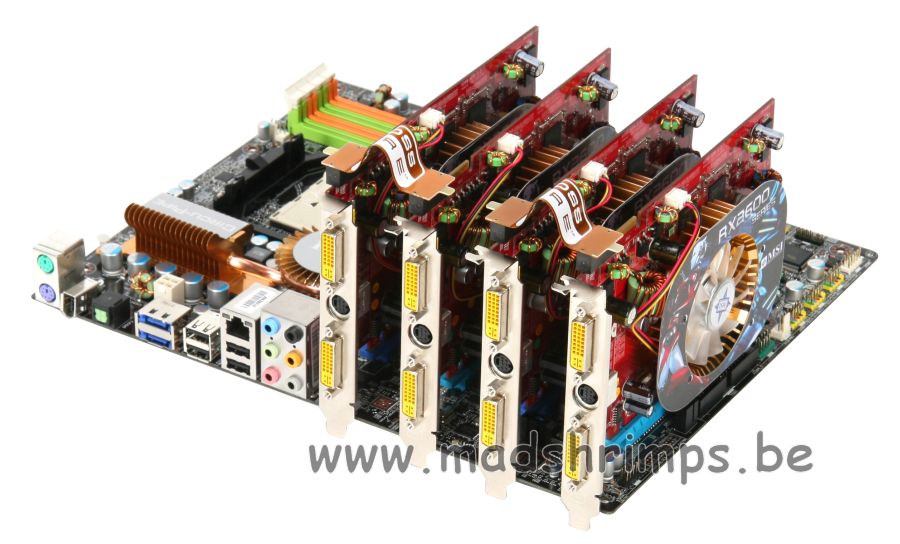

Dual-channel crossfire system
For standard high-speed serial buses such as PCIE, SATA, DDR, and USB, board manufacturers usually use Intel's Sigtest to test. Since Sigtest can analyze the waveforms captured by oscilloscopes from Agilent, Tektronix, and LeCroy, the oscilloscope is only used as a data acquisition card, which greatly reduces the dependence on the instrument (due to differences in eye diagrams and jitter analysis algorithms of oscilloscope manufacturers, the test results are inconsistent or not comparable). At the same time, sigtest can generate standard test reports, which are very popular among manufacturers. However, sigtest is not very suitable for debugging, because the data that can be analyzed by sigtest is limited, and the PLL bandwidth that can be set is also limited. It is only suitable for consistency testing of motherboards and graphics cards. The test interface is as follows:
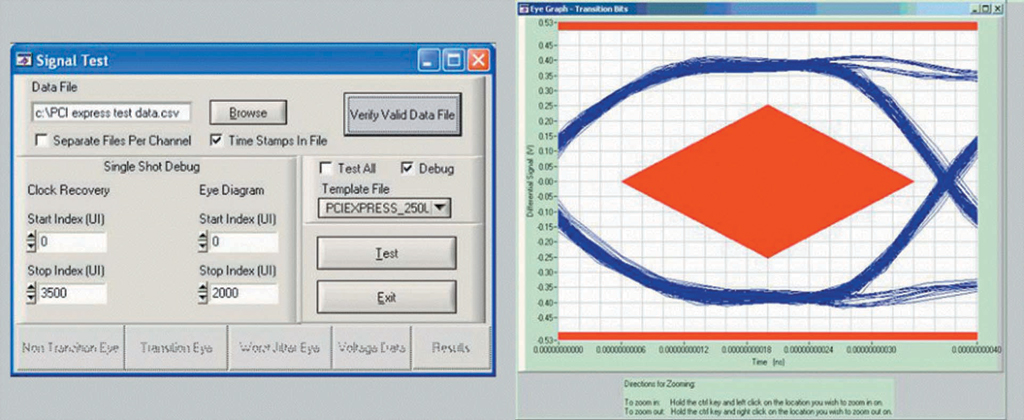
Reference address:High-speed buses and testing requirements on PC chipsets
1 X58

Intel's X58 chipset is the most advanced chipset on PC today, and is also the only chipset that supports Intel I7 CPU. In addition to integrating the most common high-speed serial bus, this chipset also has a major feature: it supports Intel's own QPI bus. The biggest difference between I7 and Intel's previous CPUs is that it integrates a memory controller like AMD K8 and supports 3-channel DDR3 memory. X58 supports 36-Lane PCIE G2, CroosFire, and can directly support SLI through NVIDIA's authorization. Let's take a look at the test requirements of these high-speed serial buses.
QPI

Intel's Quick Path Interface was first introduced on the I7 CPU, using peer-to-peer transmission similar to PCIE, replacing the previous parallel FSB. There are two bit rates for QPI: 4.8Gbps and 6.4Gbps. For 6.4Gbps QPI, when 32bit transmission is used, the bandwidth can reach 25.6GB/s. Compared to the 1600MHz FSB bandwidth of 12.8GB/s, the bandwidth has doubled. It is also better than AMD's HT 3.0 with a bit rate of 5.2Gbps and a bandwidth of 20.8GB/s when transmitting 32bit. At the same time, QPI can not only be used for the interconnection between the CPU and the north bridge chip, but also for the internal interconnection between multi-core processors and the interconnection with the memory controller.
Since the fundamental wave of QPI 6.4Gbps is 3.2GHz, the 1.8bit rate is 11.52GHz, and the 5th harmonic is 16GHz, an oscilloscope with a bandwidth of 16GHz is required for testing. Tektronix and LeCroy both have oscilloscopes with bandwidths above 16GHz, but LeCroy currently has no QPI test solution. Tektronix is the first company in the industry to launch an oscilloscope-based QPI test solution, while Agilent has launched the bit error rate tester J-BERT N4903B.

PCI Express 2.0
PCIE G2 has a bit rate of 5Gbps, a fundamental frequency of 2.5GHz, a 1.8x bit rate of 9GHz, and a 5th harmonic of 12.5GHz. Except for Agilent DSO91304, which has a bandwidth of only 13GHz, which just meets the requirement of the 5th harmonic, Tektronix and LeCroy both have oscilloscopes with bandwidths above 12.5GHz, and Tektronix's oscilloscopes are more popular among board manufacturers.
SATA 3Gbps
SATA 3Gbps, commonly known as SATA 2, has a fundamental frequency of 1.5GHz, a 1.8x bit rate of 5.4GHz, and a 5th harmonic of 7.5GHz. It requires an oscilloscope with a bandwidth of 8GHz, which can be met by Agilent, Tekronix, and LeCroy.
DDR3
DDR3 starts at 800MHz, and the highest that meets the specification is 1600MHz. X58 supports DDR3-1066 with a bandwidth of 8.5GB/S, a bit rate of 1.066Gbps, a fundamental wave of 533MHz, a 1.8x bit rate of 1.9188GHz, and a fifth harmonic of 2665. Agilent and Tektronix have both launched DDR3 test solutions.
USB 2.0 High SpeedUSB 2.0 can be said to be the entry-level high-speed serial bus, with a bit rate of only 480Mbps, a fundamental wave of 240MHz, a 1.8x bit rate of 864MHz, and a fifth harmonic of 1.2GHz. In fact, the USB certification organization believes that an oscilloscope with a bandwidth of 1GHz can meet the consistency test of USB2.0 High Speed.
In addition, the DMI bus between X58 and ICH10 is based on PCIE G2 x4, with a bandwidth of 2GB/s, which is similar to AMD's A-link interconnection between the north and south bridges (also based on PCIE G2 X4).
2. RD790FX
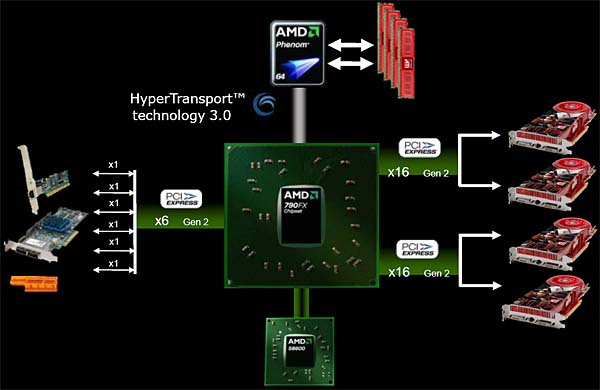
Compared with x58, AMD's competing product is RD790, and the most advanced one is RD790FX. 790FX natively supports 40 Lane PCIE G2, of which 32 lanes are allocated to graphics cards to form 2x16 and 4x8 crossfire, 6 lanes are allocated to peripherals, and the other 4 lanes form Alink to connect the north and south bridges.

The difference from X58 is that the CPU and RD790FX are connected via HT 3.0, and the memory only supports DDR2.

Dual-channel crossfire system
For standard high-speed serial buses such as PCIE, SATA, DDR, and USB, board manufacturers usually use Intel's Sigtest to test. Since Sigtest can analyze the waveforms captured by oscilloscopes from Agilent, Tektronix, and LeCroy, the oscilloscope is only used as a data acquisition card, which greatly reduces the dependence on the instrument (due to differences in eye diagrams and jitter analysis algorithms of oscilloscope manufacturers, the test results are inconsistent or not comparable). At the same time, sigtest can generate standard test reports, which are very popular among manufacturers. However, sigtest is not very suitable for debugging, because the data that can be analyzed by sigtest is limited, and the PLL bandwidth that can be set is also limited. It is only suitable for consistency testing of motherboards and graphics cards. The test interface is as follows:

Previous article:Classification of EMC electromagnetic compatibility testing laboratories
Next article:Communication test solution
- Popular Resources
- Popular amplifiers
Recommended Content
Latest Test Measurement Articles
- New IsoVu™ Isolated Current Probes: Bringing a New Dimension to Current Measurements
- Modern manufacturing strategies drive continuous improvement in ICT online testing
- Methods for Correlation of Contact and Non-Contact Measurements
- Keysight Technologies Helps Samsung Electronics Successfully Validate FiRa® 2.0 Safe Distance Measurement Test Case
- From probes to power supplies, Tektronix is leading the way in comprehensive innovation in power electronics testing
- Seizing the Opportunities in the Chinese Application Market: NI's Challenges and Answers
- Tektronix Launches Breakthrough Power Measurement Tools to Accelerate Innovation as Global Electrification Accelerates
- Not all oscilloscopes are created equal: Why ADCs and low noise floor matter
- Enable TekHSI high-speed interface function to accelerate the remote transmission of waveform data
MoreSelected Circuit Diagrams
MorePopular Articles
- Intel promotes AI with multi-dimensional efforts in technology, application, and ecology
- ChinaJoy Qualcomm Snapdragon Theme Pavilion takes you to experience the new changes in digital entertainment in the 5G era
- Infineon's latest generation IGBT technology platform enables precise control of speed and position
- Two test methods for LED lighting life
- Don't Let Lightning Induced Surges Scare You
- Application of brushless motor controller ML4425/4426
- Easy identification of LED power supply quality
- World's first integrated photovoltaic solar system completed in Israel
- Sliding window mean filter for avr microcontroller AD conversion
- What does call mean in the detailed explanation of ABB robot programming instructions?
MoreDaily News
- STMicroelectronics discloses its 2027-2028 financial model and path to achieve its 2030 goals
- 2024 China Automotive Charging and Battery Swapping Ecosystem Conference held in Taiyuan
- State-owned enterprises team up to invest in solid-state battery giant
- The evolution of electronic and electrical architecture is accelerating
- The first! National Automotive Chip Quality Inspection Center established
- BYD releases self-developed automotive chip using 4nm process, with a running score of up to 1.15 million
- GEODNET launches GEO-PULSE, a car GPS navigation device
- Should Chinese car companies develop their own high-computing chips?
- Infineon and Siemens combine embedded automotive software platform with microcontrollers to provide the necessary functions for next-generation SDVs
- Continental launches invisible biometric sensor display to monitor passengers' vital signs
Guess you like
- TI - MCU - MSP430 User Guide 6 -> CS Clock System
- Allegro--bundle setting problem
- STM32MP1(1)--CM4 MDK debugging project sharing
- Phase relationship of field effect tube
- TMS320F28379D User Experience SCI
- ? A general question. How does this varactor diode represent?
- [STM32F1] STM32 configuration file problem
- Xilinx FPGA(CPLD) Download Cable Schematic
- How to use wire connectors?
- 7.5KW motor hard start problem?

 【Maxim】MAX13041: ±80V Fault-Protected, Sleep-Mode CAN Transceiver
【Maxim】MAX13041: ±80V Fault-Protected, Sleep-Mode CAN Transceiver
















 京公网安备 11010802033920号
京公网安备 11010802033920号